Pull Dog: Automatic Docker Test Environments for Pull Requests
WrittenPull Dog is a GitHub app that will automatically provision a Docker-based test server for your feature as you open a pull request. And best of all - it's all free!
Today, almost every developer is using a managed Git service like GitHub. When writing code, this is almost essential, no matter if you're alone or in a team.
But there are many ways to organize code. What I've seen most people do is to branch out when they make a new feature, and create a "Pull Request" when they have finished that feature.
This allows for several benefits:
- Someone can review the code before it is merged.
- Someone can clone the code and test it on their machine, to make sure nothing broke.
But that second step can be quite tedious and annoying, especially if the person that needs to test the feature is not a developer.
This is where Pull Dog comes in to play.

Pull Dog is a GitHub app that will automatically provision a Docker-based test server for your feature as you open a pull request. And best of all - it's all free!
Setting it up
You start out by installing the app to your GitHub account.
Once installed, you simply push a commit to the master branch of the repository you want to enable, with a pull-dog.json file in the root directory that contains the following.
{
"dockerComposeYmlFilePaths": [
"your/path/to/docker-compose.yml"
]
}
After pushing, Pull Dog is enabled for the given repository and will run for any future pull requests that are opened.
Trying it out
For my example, I made an empty repository with the following pull-dog.json configuration file:
{
"dockerComposeYmlFilePaths": [
"docker-compose.yml"
]
}
And the following docker-compose.yml file, containing a basic WordPress and MySQL setup.
version: '3.3'
services:
db:
image: mysql:5.7
volumes:
- db_data:/var/lib/mysql
restart: always
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: somewordpress
MYSQL_DATABASE: wordpress
MYSQL_USER: wordpress
MYSQL_PASSWORD: wordpress
wordpress:
depends_on:
- db
image: wordpress:latest
ports:
- "8000:80"
restart: always
environment:
WORDPRESS_DB_HOST: db:3306
WORDPRESS_DB_USER: wordpress
WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD: wordpress
WORDPRESS_DB_NAME: wordpress
volumes:
db_data: {}
Opening a pull request
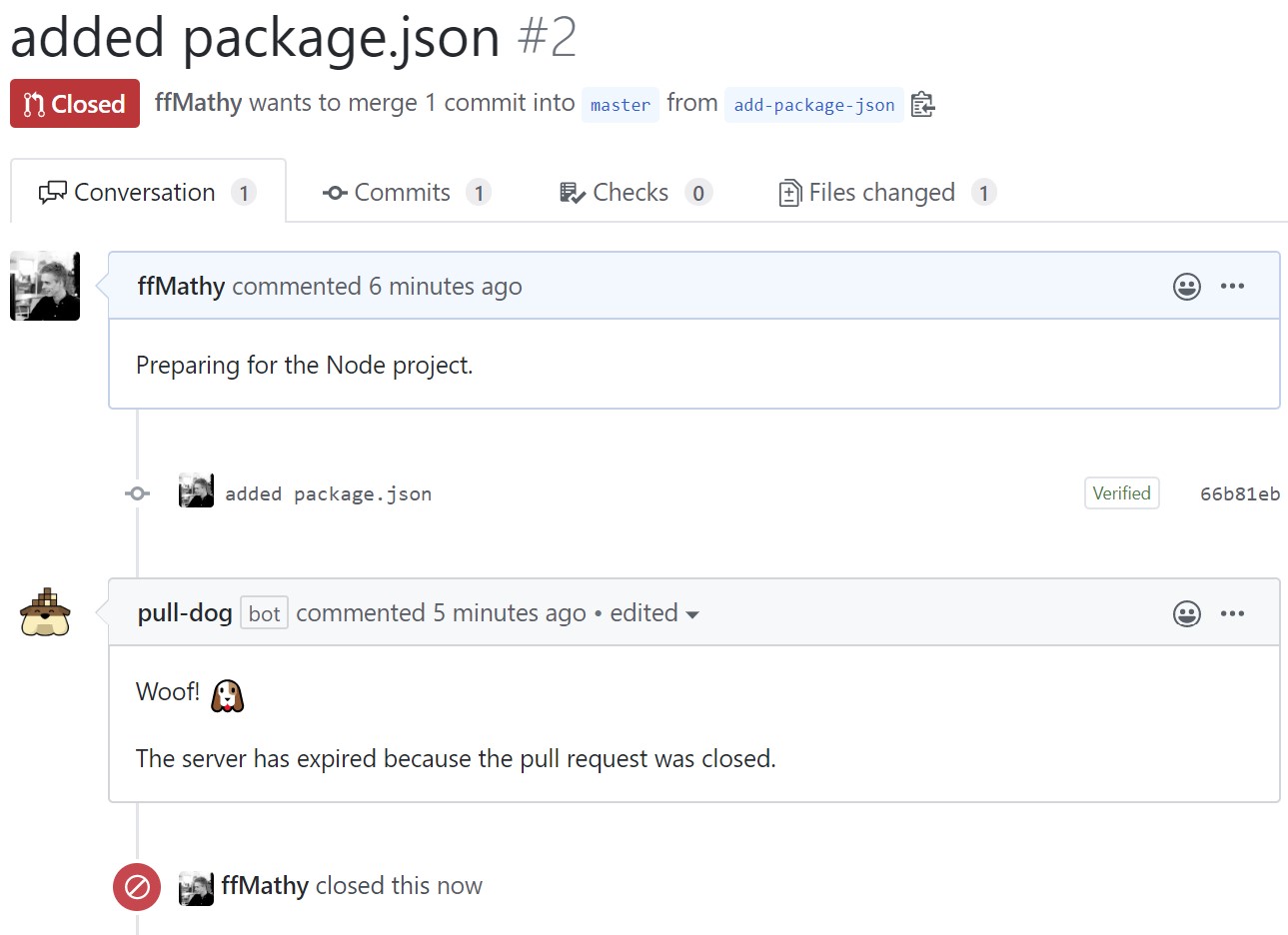
Upon opening my pull request, I am greeted with the following comment from pull-dog where I can see that it is provisioning a server for me.
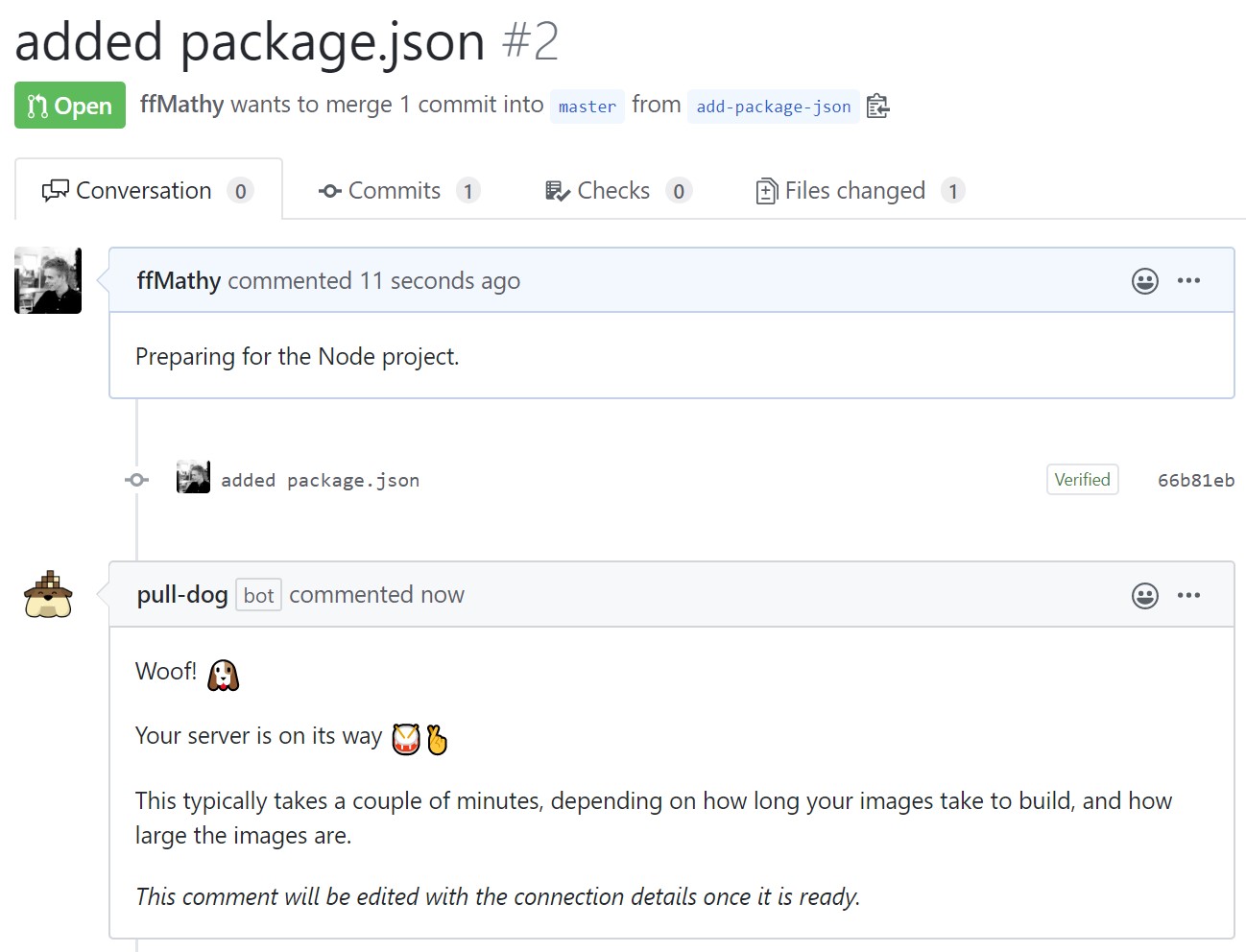
After a brief while, the comment is updated with the connection details of my server. Note that the port 8000 is the exposed port from the docker-compose.yml file.
Closing the pull request
After closing the pull request, the server is shut down again, and the comment is updated to reflect that.